
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-487736919-59a03eab22fa3a00102ca64e.jpg)
Hastaların yaş ve cinsiyet dağılımları arasında anlamlı bir fark bulunmadı. Bulgular: Çalışmaya 40 hasta dahil edildi. Timpanometri ile basınç, volüm, kompliyans değerleri ölçülerek ameliyat öncesi ve sonrası değerler karşılaştırıldı. Grup 1 hastalara transnazal basınçlı irrigasyon, grup 2 hastalara transoral pasif irrigasyon yapıldı. Hastalar ameliyat sonrası nazofarenks irrigasyonuna göre iki gruba ayrıldı.
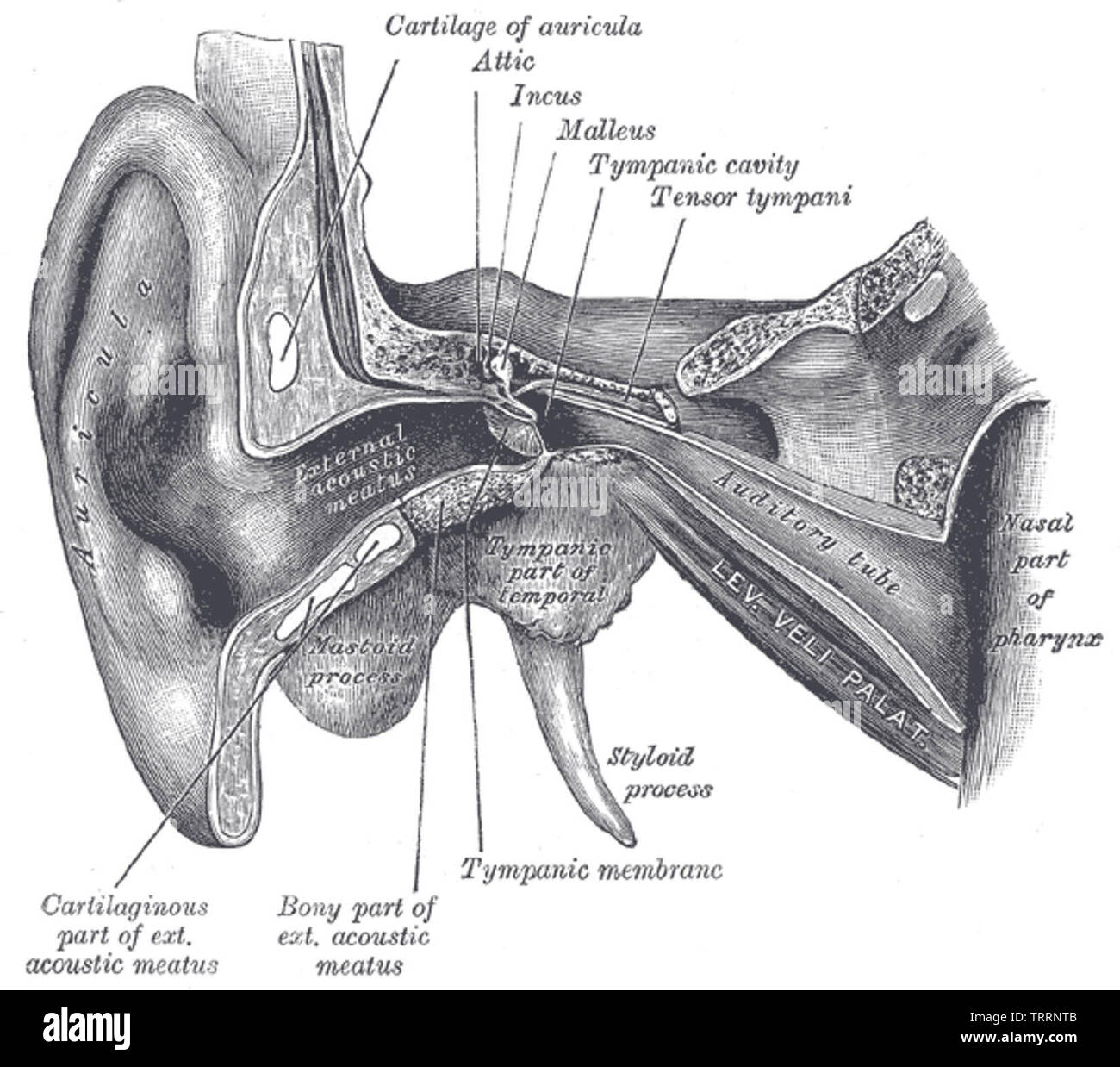
Yöntem: Adenoid hipertrofisi nedeniyle opere edilen hastaların ameliyat öncesi ve ameliyat sonrası birinci gün otomikroskopik muayene ve timpanometri ile östaki tüp fonksiyonları değerlendirildi. Bu çalışmada adenoidektomi yapılan hastalarda kanama kontrolü için yapılan nazofarenks irrigasyonunun östaki tüp fonksiyonlarına etkisinin olup olmadığını araştırmayı amaçladık.
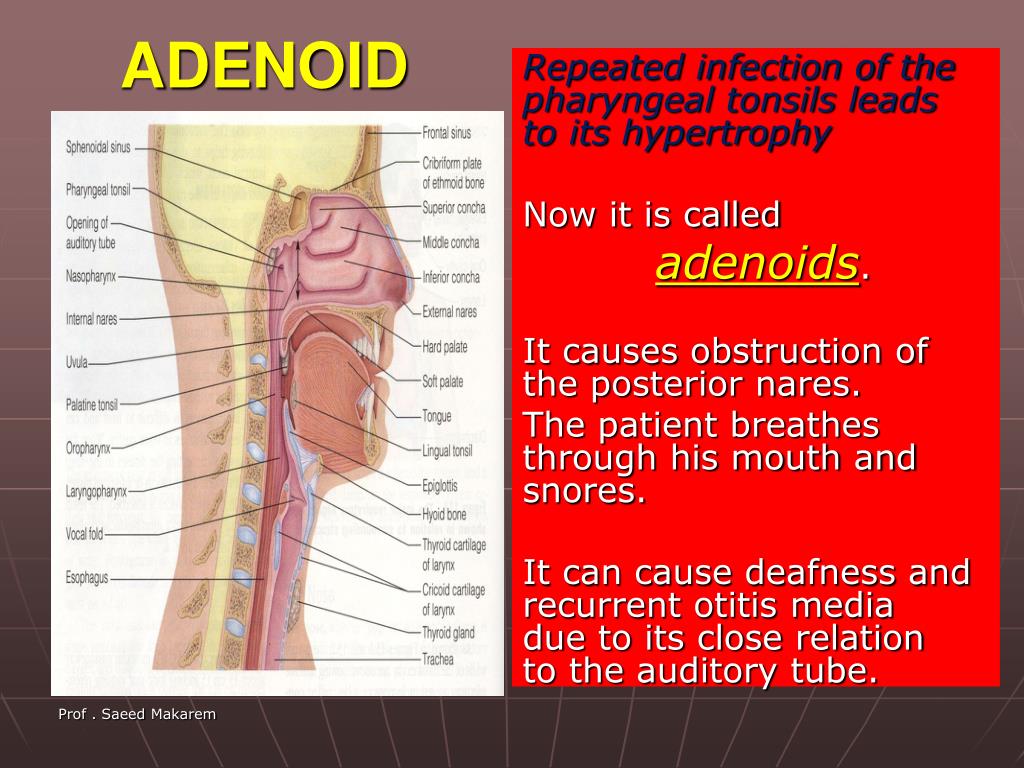
Adenoidektomi, tonsillektomi ile birlikte çocuklarda yapılan en sık cerrahi prosedürdür.
Adenoid auditory tube series#
However, in group 2, right side type B, left sidetype B and bilateral type C tympanogram were observed in 1 patient, 2patients and 12 patients, respectively.Conclusion: In this study, we observed that the nasopharyngealirrigation to control bleeding after adenoidectomy had adverse effect onthe eustachian tube functions but larger series of studies are needed toconfirm this Anahtar Kelime:Īmaç: Adenoid dokunun hipertrofisi, mekanik veya enflamatuvar süreçlerden dolayı östaki tüpünün nazofaringeal ağzını obstrükte ederek östaki disfonksiyonuna yol açmaktadır. Postoperative tympanometry types were seen as bilateral type C in 7 patients, as rightside type C in 4 patients, as bilateral type B in 2 patients, as left side typeC in 4 patients in group 1. The mean pressure values of the tympanometry parameterswere highly significantly different for the right ear and moderately differentfor the left ear in group 1 were significantly different for the right earand highly significantly different for the left ear in group 2. Volumeand compliance values between the groups were similar before and afterthe surgery. There was no significantdifference between the age and sex distributions of the patients.
Tympanometry was used to measure pressure, volumetric, andcompliance values to compare pre- and postoperative values.Results: 40 patients were included in the study. Group 1 was the transnasalpressure irrigation group group 2 was transoral passive irrigationgroup. Patients were divided into two groups according tonasopharyngeal irrigation type after surgery. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether nasopharyngealirrigation for hemorrhage control in adenoidectomy patients has an effecton eustachian tube functions.Method: Patients who underwent adenoidectomy for adenoid hypertrophyevaluated on both the preoperatively and on the postoperative first dayby otomicroscopic examination and with tympanometry for eustachiantube functions. Adenoidectomy,with or without tonsillectomy, is the most common surgical procedure inchildren. Objective: The hypertrophic adenoid tissue can cause to eustachiantube dysfunction by mechanical or inflammatory effect both of whichblock the nasopharyngeal ostium of the eustachian tube.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
